在上一讲中,我们学习了如何利用 numpy 手动搭建卷积神经网络。但在实际的图像识别中,使用 numpy 去手写 CNN 未免有些吃力不讨好。在 DNN 的学习中,我们也是在手动搭建之后利用 Tensorflow 去重新实现一遍,一来为了能够对神经网络的传播机制能够理解更加透彻,二来也是为了更加高效使用开源框架快速搭建起深度学习项目。本节就继续和大家一起学习如何利用 Tensorflow 搭建一个卷积神经网络。
我们继续以 NG 课题组提供的 sign 手势数据集为例,学习如何通过 Tensorflow 快速搭建起一个深度学习项目。数据集标签共有零到五总共 6 类标签,示例如下:
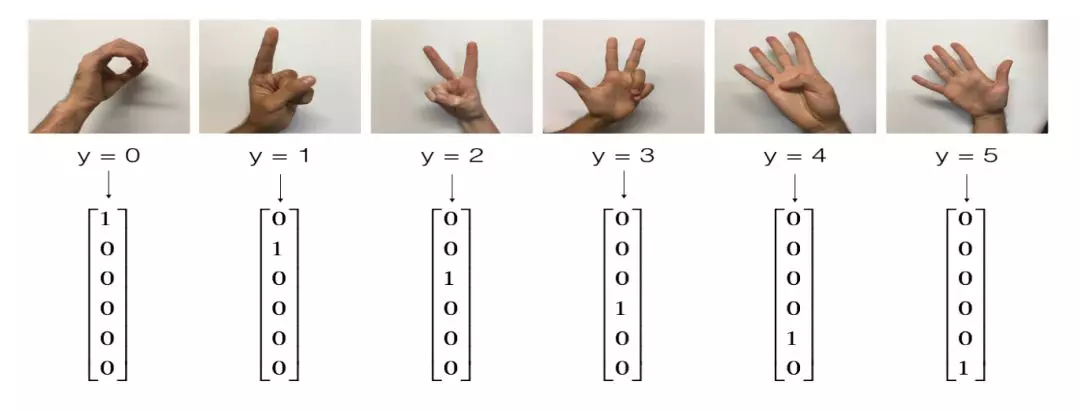
先对数据进行简单的预处理并查看训练集和测试集维度:
X_train = X_train_orig/255.
X_test = X_test_orig/255.
Y_train = convert_to_one_hot(Y_train_orig, 6).T
Y_test = convert_to_one_hot(Y_test_orig, 6).T
print ("number of training examples = " + str(X_train.shape[0]))
print ("number of test examples = " + str(X_test.shape[0]))
print ("X_train shape: " + str(X_train.shape))
print ("Y_train shape: " + str(Y_train.shape))
print ("X_test shape: " + str(X_test.shape))
print ("Y_test shape: " + str(Y_test.shape))
可见我们总共有 1080 张 64643 训练集图像,120 张 64643 的测试集图像,共有 6 类标签。下面我们开始搭建过程。
创建 placeholder
首先需要为训练集预测变量和目标变量创建占位符变量 placeholder ,定义创建占位符变量函数:
def create_placeholders(n_H0, n_W0, n_C0, n_y):
"""
Creates the placeholders for the tensorflow session.
Arguments:
n_H0 -- scalar, height of an input image
n_W0 -- scalar, width of an input image
n_C0 -- scalar, number of channels of the input
n_y -- scalar, number of classes
Returns:
X -- placeholder for the data input, of shape [None, n_H0, n_W0, n_C0] and dtype "float"
Y -- placeholder for the input labels, of shape [None, n_y] and dtype "float"
"""
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(None, n_H0, n_W0, n_C0), name='X')
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(None, n_y), name='Y')
return X, Y参数初始化
然后需要对滤波器权值参数进行初始化:
def initialize_parameters():
"""
Initializes weight parameters to build a neural network with tensorflow.
Returns:
parameters -- a dictionary of tensors containing W1, W2
"""
tf.set_random_seed(1)
W1 = tf.get_variable("W1", [4,4,3,8], initializer = tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer(seed = 0))
W2 = tf.get_variable("W2", [2,2,8,16], initializer = tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer(seed = 0))
parameters = {"W1": W1,
"W2": W2}
return parameters执行卷积网络的前向传播过程
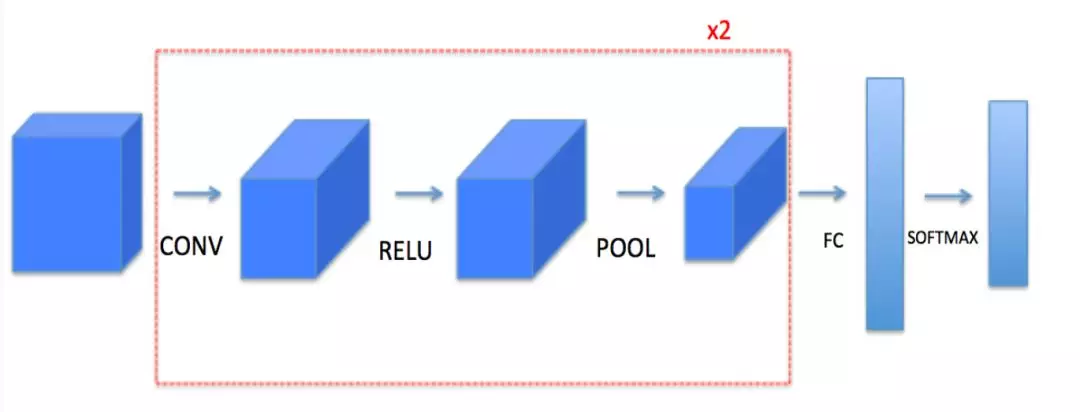
前向传播过程如下所示:
CONV2D -> RELU -> MAXPOOL -> CONV2D -> RELU -> MAXPOOL -> FLATTEN -> FULLYCONNECTED
可见我们要搭建的是一个典型的 CNN 过程,经过两次的卷积-relu激活-最大池化,然后展开接上一个全连接层。利用 Tensorflow 搭建上述传播过程如下:
def forward_propagation(X, parameters):
"""
Implements the forward propagation for the model
Arguments:
X -- input dataset placeholder, of shape (input size, number of examples)
parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters "W1", "W2"
the shapes are given in initialize_parameters
Returns:
Z3 -- the output of the last LINEAR unit
"""
# Retrieve the parameters from the dictionary "parameters"
W1 = parameters['W1']
W2 = parameters['W2']
# CONV2D: stride of 1, padding 'SAME'
Z1 = tf.nn.conv2d(X,W1, strides = [1,1,1,1], padding = 'SAME')
# RELU
A1 = tf.nn.relu(Z1)
# MAXPOOL: window 8x8, sride 8, padding 'SAME'
P1 = tf.nn.max_pool(A1, ksize = [1,8,8,1], strides = [1,8,8,1], padding = 'SAME')
# CONV2D: filters W2, stride 1, padding 'SAME'
Z2 = tf.nn.conv2d(P1,W2, strides = [1,1,1,1], padding = 'SAME')
# RELU
A2 = tf.nn.relu(Z2)
# MAXPOOL: window 4x4, stride 4, padding 'SAME'
P2 = tf.nn.max_pool(A2, ksize = [1,4,4,1], strides = [1,4,4,1], padding = 'SAME')
# FLATTEN
P2 = tf.contrib.layers.flatten(P2)
Z3 = tf.contrib.layers.fully_connected(P2, 6, activation_fn = None)
return Z3计算当前损失
在 Tensorflow 中计算损失函数非常简单,一行代码即可:
def compute_cost(Z3, Y):
"""
Computes the cost
Arguments:
Z3 -- output of forward propagation (output of the last LINEAR unit), of shape (6, number of examples)
Y -- "true" labels vector placeholder, same shape as Z3
Returns:
cost - Tensor of the cost function
"""
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=Z3, labels=Y))
return cost 定义好上述过程之后,就可以封装整体的训练过程模型。可能你会问为什么没有反向传播,这里需要注意的是 Tensorflow 帮助我们自动封装好了反向传播过程,无需我们再次定义,在实际搭建过程中我们只需将前向传播的网络结构定义清楚即可。
封装模型
def model(X_train, Y_train, X_test, Y_test, learning_rate = 0.009,
num_epochs = 100, minibatch_size = 64, print_cost = True):
"""
Implements a three-layer ConvNet in Tensorflow:
CONV2D -> RELU -> MAXPOOL -> CONV2D -> RELU -> MAXPOOL -> FLATTEN -> FULLYCONNECTED
Arguments:
X_train -- training set, of shape (None, 64, 64, 3)
Y_train -- test set, of shape (None, n_y = 6)
X_test -- training set, of shape (None, 64, 64, 3)
Y_test -- test set, of shape (None, n_y = 6)
learning_rate -- learning rate of the optimization
num_epochs -- number of epochs of the optimization loop
minibatch_size -- size of a minibatch
print_cost -- True to print the cost every 100 epochs
Returns:
train_accuracy -- real number, accuracy on the train set (X_train)
test_accuracy -- real number, testing accuracy on the test set (X_test)
parameters -- parameters learnt by the model. They can then be used to predict.
"""
ops.reset_default_graph()
tf.set_random_seed(1)
seed = 3
(m, n_H0, n_W0, n_C0) = X_train.shape
n_y = Y_train.shape[1]
costs = []
# Create Placeholders of the correct shape
X, Y = create_placeholders(n_H0, n_W0, n_C0, n_y)
# Initialize parameters
parameters = initialize_parameters()
# Forward propagation
Z3 = forward_propagation(X, parameters)
# Cost function
cost = compute_cost(Z3, Y)
# Backpropagation
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate = learning_rate).minimize(cost) # Initialize all the variables globally
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# Start the session to compute the tensorflow graph
with tf.Session() as sess:
# Run the initialization
sess.run(init)
# Do the training loop
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
minibatch_cost = 0.
num_minibatches = int(m / minibatch_size)
seed = seed + 1
minibatches = random_mini_batches(X_train, Y_train, minibatch_size, seed)
for minibatch in minibatches:
# Select a minibatch
(minibatch_X, minibatch_Y) = minibatch
_ , temp_cost = sess.run([optimizer, cost], feed_dict={X: minibatch_X, Y: minibatch_Y})
minibatch_cost += temp_cost / num_minibatches
# Print the cost every epoch
if print_cost == True and epoch % 5 == 0:
print ("Cost after epoch %i: %f" % (epoch, minibatch_cost))
if print_cost == True and epoch % 1 == 0:
costs.append(minibatch_cost)
# plot the cost
plt.plot(np.squeeze(costs))
plt.ylabel('cost')
plt.xlabel('iterations (per tens)')
plt.title("Learning rate =" + str(learning_rate))
plt.show() # Calculate the correct predictions
predict_op = tf.argmax(Z3, 1)
correct_prediction = tf.equal(predict_op, tf.argmax(Y, 1))
# Calculate accuracy on the test set
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float"))
print(accuracy)
train_accuracy = accuracy.eval({X: X_train, Y: Y_train})
test_accuracy = accuracy.eval({X: X_test, Y: Y_test})
print("Train Accuracy:", train_accuracy)
print("Test Accuracy:", test_accuracy)
return train_accuracy, test_accuracy, parameters对训练集执行模型训练:
_, _, parameters = model(X_train, Y_train, X_test, Y_test)训练迭代过程如下:
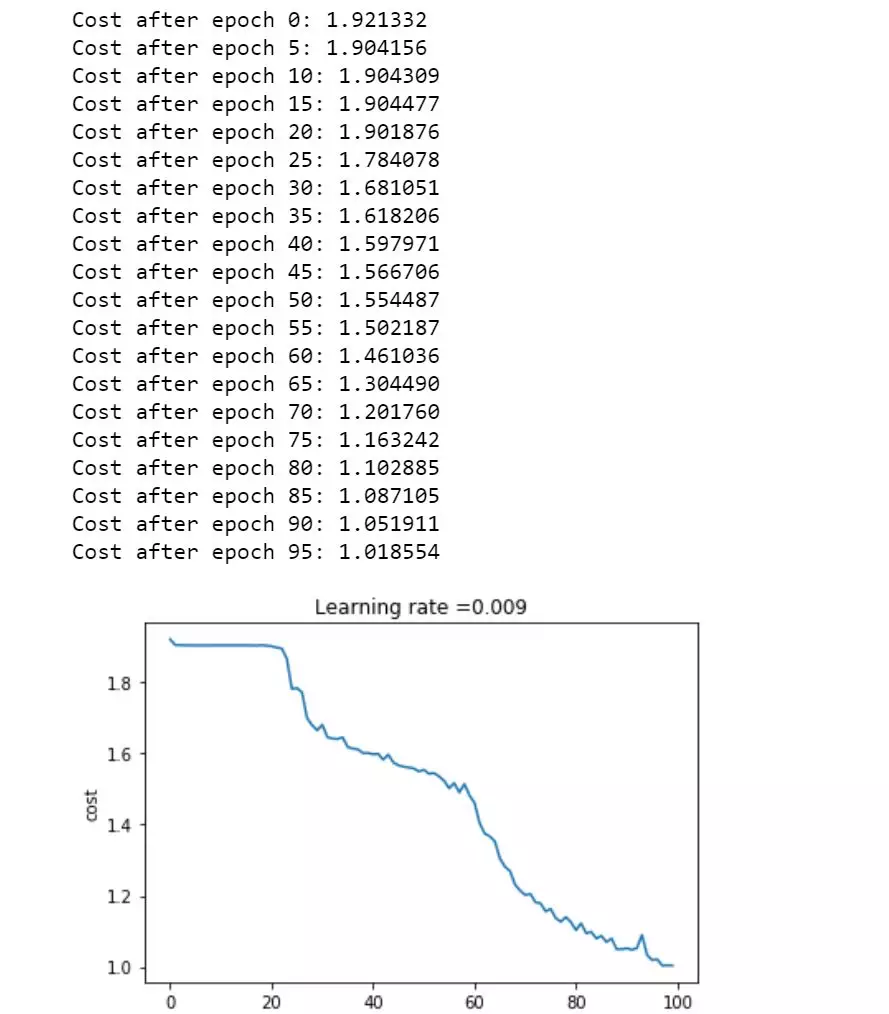

我们在训练集上取得了 0.67 的准确率,在测试集上的预测准确率为 0.58 ,虽然效果并不显著,模型也有待深度调优,但我们已经学会了如何用 Tensorflow 快速搭建起一个深度学习系统了。
注:本深度学习笔记系作者学习 Andrew NG 的 deeplearningai 五门课程所记笔记,其中代码为每门课的课后assignments作业整理而成。
参考资料:
https://www.coursera.org/learn/machine-learning
