from __future__ import print_function
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.cbook as cbook
import matplotlib.image as image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
datafile = cbook.get_sample_data('logo2.png', asfileobj=False)
print('loading %s' % datafile)
im = image.imread(datafile)
im[:, :, -1] = 0.5 # set the alpha channel
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(np.random.rand(20), '-o', ms=20, lw=2, alpha=0.7, mfc='orange')
ax.grid()
fig.figimage(im, 10, 10, zorder=3)
plt.show()
2. 函数散点图
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.gca(projection='3d')
# Plot a sin curve using the x and y axes.
x = np.linspace(0, 1, 100)
y = np.sin(x * 2 * np.pi) / 2 + 0.5
ax.plot(x, y, zs=0, zdir='z', label='curve in (x,y)')
# Plot scatterplot data (20 2D points per colour) on the x and z axes.
colors = ('r', 'g', 'b', 'k')
x = np.random.sample(20*len(colors))
y = np.random.sample(20*len(colors))
c_list = []
for c in colors:
c_list.append([c]*20)
# By using zdir='y', the y value of these points is fixed to the zs value 0
# and the (x,y) points are plotted on the x and z axes.
ax.scatter(x, y, zs=0, zdir='y', c=c_list, label='points in (x,z)')
# Make legend, set axes limits and labels
ax.legend()
ax.set_xlim(0, 1)
ax.set_ylim(0, 1)
ax.set_zlim(0, 1)
ax.set_xlabel('X')
ax.set_ylabel('Y')
ax.set_zlabel('Z')
# Customize the view angle so it's easier to see that the scatter points lie
# on the plane y=0
ax.view_init(elev=20., azim=-35)
plt.show()
3. 三维曲面图
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
import matplotlib.tri as mtri
fig = plt.figure(figsize=plt.figaspect(0.5))
#============
# First plot
#============
# Make a mesh in the space of parameterisation variables u and v
u = np.linspace(0, 2.0 * np.pi, endpoint=True, num=50)
v = np.linspace(-0.5, 0.5, endpoint=True, num=10)
u, v = np.meshgrid(u, v)
u, v = u.flatten(), v.flatten()
# This is the Mobius mapping, taking a u, v pair and returning an x, y, z
# triple
x = (1 + 0.5 * v * np.cos(u / 2.0)) * np.cos(u)
y = (1 + 0.5 * v * np.cos(u / 2.0)) * np.sin(u)
z = 0.5 * v * np.sin(u / 2.0)
# Triangulate parameter space to determine the triangles
tri = mtri.Triangulation(u, v)
# Plot the surface. The triangles in parameter space determine which x, y, z
# points are connected by an edge.
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 1, projection='3d')
ax.plot_trisurf(x, y, z, triangles=tri.triangles, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral)
ax.set_zlim(-1, 1)
#============
# Second plot
#============
# Make parameter spaces radii and angles.
n_angles = 36
n_radii = 8
min_radius = 0.25
radii = np.linspace(min_radius, 0.95, n_radii)
angles = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, n_angles, endpoint=False)
angles = np.repeat(angles[..., np.newaxis], n_radii, axis=1)
angles[:, 1::2] += np.pi/n_angles
# Map radius, angle pairs to x, y, z points.
x = (radii*np.cos(angles)).flatten()
y = (radii*np.sin(angles)).flatten()
z = (np.cos(radii)*np.cos(angles*3.0)).flatten()
# Create the Triangulation; no triangles so Delaunay triangulation created.
triang = mtri.Triangulation(x, y)
# Mask off unwanted triangles.
xmid = x[triang.triangles].mean(axis=1)
ymid = y[triang.triangles].mean(axis=1)
mask = np.where(xmid**2 + ymid**2 < min_radius**2, 1, 0)
triang.set_mask(mask)
# Plot the surface.
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 2, projection='3d')
ax.plot_trisurf(triang, z, cmap=plt.cm.CMRmap)
plt.show()
4. 地形地貌
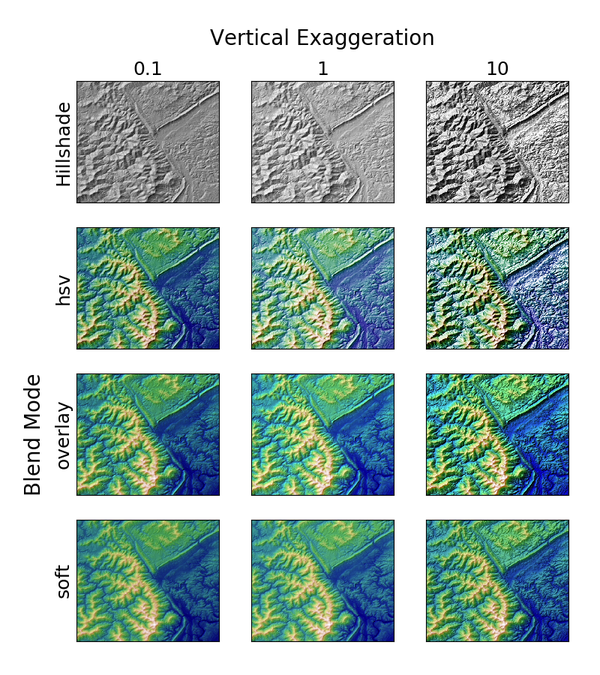
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.cbook import get_sample_data
from matplotlib.colors import LightSource
dem = np.load(get_sample_data('jacksboro_fault_dem.npz'))
z = dem['elevation']
#-- Optional dx and dy for accurate vertical exaggeration --------------------
# If you need topographically accurate vertical exaggeration, or you don't want
# to guess at what *vert_exag* should be, you'll need to specify the cellsize
# of the grid (i.e. the *dx* and *dy* parameters). Otherwise, any *vert_exag*
# value you specify will be relative to the grid spacing of your input data
# (in other words, *dx* and *dy* default to 1.0, and *vert_exag* is calculated
# relative to those parameters). Similarly, *dx* and *dy* are assumed to be in
# the same units as your input z-values. Therefore, we'll need to convert the
# given dx and dy from decimal degrees to meters.
dx, dy = dem['dx'], dem['dy']
dy = 111200 * dy
dx = 111200 * dx * np.cos(np.radians(dem['ymin']))
#-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Shade from the northwest, with the sun 45 degrees from horizontal
ls = LightSource(azdeg=315, altdeg=45)
cmap = plt.cm.gist_earth
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=4, ncols=3, figsize=(8, 9))
plt.setp(axes.flat, xticks=[], yticks=[])
# Vary vertical exaggeration and blend mode and plot all combinations
for col, ve in zip(axes.T, [0.1, 1, 10]):
# Show the hillshade intensity image in the first row
col[0].imshow(ls.hillshade(z, vert_exag=ve, dx=dx, dy=dy), cmap='gray')
# Place hillshaded plots with different blend modes in the rest of the rows
for ax, mode in zip(col[1:], ['hsv', 'overlay', 'soft']):
rgb = ls.shade(z, cmap=cmap, blend_mode=mode,
vert_exag=ve, dx=dx, dy=dy)
ax.imshow(rgb)
# Label rows and columns
for ax, ve in zip(axes[0], [0.1, 1, 10]):
ax.set_title('{0}'.format(ve), size=18)
for ax, mode in zip(axes[:, 0], ['Hillshade', 'hsv', 'overlay', 'soft']):
ax.set_ylabel(mode, size=18)
# Group labels...
axes[0, 1].annotate('Vertical Exaggeration', (0.5, 1), xytext=(0, 30),
textcoords='offset points', xycoords='axes fraction',
ha='center', va='bottom', size=20)
axes[2, 0].annotate('Blend Mode', (0, 0.5), xytext=(-30, 0),
textcoords='offset points', xycoords='axes fraction',
ha='right', va='center', size=20, rotation=90)
fig.subplots_adjust(bottom=0.05, right=0.95)
plt.show()
5. 统计图
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
np.random.seed(0)
n_bins = 10
x = np.random.randn(1000, 3)
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=2)
ax0, ax1, ax2, ax3 = axes.flatten()
colors = ['red', 'tan', 'lime']
ax0.hist(x, n_bins, normed=1, histtype='bar', color=colors, label=colors)
ax0.legend(prop={'size': 10})
ax0.set_title('bars with legend')
ax1.hist(x, n_bins, normed=1, histtype='bar', stacked=True)
ax1.set_title('stacked bar')
ax2.hist(x, n_bins, histtype='step', stacked=True, fill=False)
ax2.set_title('stack step (unfilled)')
# Make a multiple-histogram of data-sets with different length.
x_multi = [np.random.randn(n) for n in [10000, 5000, 2000]]
ax3.hist(x_multi, n_bins, histtype='bar')
ax3.set_title('different sample sizes')
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
6. 形状和集合
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcdefaults()
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.path as mpath
import matplotlib.lines as mlines
import matplotlib.patches as mpatches
from matplotlib.collections import PatchCollection
def label(xy, text):
y = xy[1] - 0.15 # shift y-value for label so that it's below the artist
plt.text(xy[0], y, text, ha="center", family='sans-serif', size=14)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
# create 3x3 grid to plot the artists
grid = np.mgrid[0.2:0.8:3j, 0.2:0.8:3j].reshape(2, -1).T
patches = []
# add a circle
circle = mpatches.Circle(grid[0], 0.1, ec="none")
patches.append(circle)
label(grid[0], "Circle")
# add a rectangle
rect = mpatches.Rectangle(grid[1] - [0.025, 0.05], 0.05, 0.1, ec="none")
patches.append(rect)
label(grid[1], "Rectangle")
# add a wedge
wedge = mpatches.Wedge(grid[2], 0.1, 30, 270, ec="none")
patches.append(wedge)
label(grid[2], "Wedge")
# add a Polygon
polygon = mpatches.RegularPolygon(grid[3], 5, 0.1)
patches.append(polygon)
label(grid[3], "Polygon")
# add an ellipse
ellipse = mpatches.Ellipse(grid[4], 0.2, 0.1)
patches.append(ellipse)
label(grid[4], "Ellipse")
# add an arrow
arrow = mpatches.Arrow(grid[5, 0] - 0.05, grid[5, 1] - 0.05, 0.1, 0.1, width=0.1)
patches.append(arrow)
label(grid[5], "Arrow")
# add a path patch
Path = mpath.Path
path_data = [
(Path.MOVETO, [0.018, -0.11]),
(Path.CURVE4, [-0.031, -0.051]),
(Path.CURVE4, [-0.115, 0.073]),
(Path.CURVE4, [-0.03 , 0.073]),
(Path.LINETO, [-0.011, 0.039]),
(Path.CURVE4, [0.043, 0.121]),
(Path.CURVE4, [0.075, -0.005]),
(Path.CURVE4, [0.035, -0.027]),
(Path.CLOSEPOLY, [0.018, -0.11])
]
codes, verts = zip(*path_data)
path = mpath.Path(verts + grid[6], codes)
patch = mpatches.PathPatch(path)
patches.append(patch)
label(grid[6], "PathPatch")
# add a fancy box
fancybox = mpatches.FancyBboxPatch(
grid[7] - [0.025, 0.05], 0.05, 0.1,
boxstyle=mpatches.BoxStyle("Round", pad=0.02))
patches.append(fancybox)
label(grid[7], "FancyBboxPatch")
# add a line
x, y = np.array([[-0.06, 0.0, 0.1], [0.05, -0.05, 0.05]])
line = mlines.Line2D(x + grid[8, 0], y + grid[8, 1], lw=5., alpha=0.3)
label(grid[8], "Line2D")
colors = np.linspace(0, 1, len(patches))
collection = PatchCollection(patches, cmap=plt.cm.hsv, alpha=0.3)
collection.set_array(np.array(colors))
ax.add_collection(collection)
ax.add_line(line)
plt.subplots_adjust(left=0, right=1, bottom=0, top=1)
plt.axis('equal')
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
本站文章版权归原作者及原出处所有 。内容为作者个人观点, 并不代表本站赞同其观点和对其真实性负责。本站是一个个人学习交流的平台,并不用于任何商业目的,如果有任何问题,请及时联系我们,我们将根据著作权人的要求,立即更正或者删除有关内容。本站拥有对此声明的最终解释权。